The variableDef element is used to define each
constant, parameter, or variable used within or generated by the defined subsystem model. It
contains attributes including the variable name (used for documentation), an XML-unique
varID identifier (used for automatic code generation), the units of
measure of the variable, and optional axis system, sign convention, alias, and symbol
declarations. Optional sub-elements include a written text description and a mathematical
description, in MathML-2 content markup, of the calculations needed to derive the variable
from other variables or function table outputs. An optional sub-element,
isOutput, serves to indicate an intermediate calculation that should be
brought out to the rest of the simulation. Another optional sub-element,
isStdAIAA, indicates the variable name is defined in the
AIAA simulation standards document. A final sub-element,
uncertainty, captures the statistical properties of a (normally constant)
parameter.
There must be a single variableDef for each and every input, output or
intermediate constant or variable within the DAVEfunc model.
variableDef+ : name, varID, units, [axisSystem, sign, alias, symbol, initialValue]
description? :
(description character data)
provenanceRef? : provID OR
provenance? :
author : name, org, [email]
address? :
(address character data)
creationDate :
(date in YYYY-MM-DD format, character data)
documentRef* : docID
modificationRef* : modID
calculation? :
math (defined in MathML2.0 DTD) :
isOutput? :
isStdAIAA? :
isState? :
isStateDeriv? :
uncertainty? : effect
(normalPDF : numSigmas | uniformPDF )
variableDef attributes:
-
name A UNICODE name for the variable (may be the same string as the
varID).varIDAn XML-legal name that is unique within the file.
unitsThe units-of-measure for the signal, using the AIAA standard units convention.
axisSystemAn optional indicator of the axis system (body, inertial, etc.) in which the signal is measured. See Section 6.5, “Additional DAVE-ML conventions” below for recommended practice for nomenclature.
signAn optional indicator of which direction is considered positive (+RWD, +UP, etc.). See the section on Section 6.5, “Additional DAVE-ML conventions” below for recommended practice for abbreviations.
symbolA UNICODE Greek symbol for the signal [to be superseded with more formal MathML or TeX element in a later release].
initialValueAn optional initial value for the parameter. This is normally specified for constant parameters only.
variableDef sub-elements:
descriptionAn optional text description of the variable.
provenanceThe optional provenance element allows the author to describe the source and history of the data within this
variableDef. Alternatively, a<provenanceRef>reference can be made to a previously definedprovenance.calculationAn optional container for the MathML content markup that describes how this variable is calculated from other variables or function table outputs. This element contains a single
mathelement which is defined in the MathML-2 markup language.isOutputThis optional element, if present, signifies that this variable needs to be passed as an output. How this is accomplished is up to the implementer. Unless specified by this element, a variable is considered an output only if it is the result of a calculation or function AND is not used elsewhere in the
DAVEfunc.isStdAIAAThis optional element, if present, signifies that this variable is one of the standard AIAA simulation variable names that are defined in the (draft) AIAA Simulation Standard Variable Names [AIAA01]. Such identification should make it easier for the importing process to connect this variable (probably an input or output of the model) to the appropriate variable to/from the user's simulation framework.
isStateThis optional element, if present, signifies that this variable serves as a state of the model.
isStateDerivThis optional element, if present, signifies that this variable serves as a state derivative of the model.
uncertaintyThis optional element, if present, describes the uncertainty of this parameter. See the section on Statistics below for more information about this element. Note that the
uncertaintysub-element makes sense only for constant parameters (e.g., those with nocalculationelement but with aninitialValuespecified.
Example 2. Two excerpts with examples of variableDef elements defining
input signals
In the excerpts below, two input variables are defined: XMACH and
DBFLL. These two variables are inputs to a table lookup function
shown in Example 11, “An excerpt giving the example of a function which refers to a previously defined
griddedTableDef” below.
<!-- ========================== -->
<!-- ==================== VARIABLE DEFINITIONS ==================== -->
<!-- ========================== -->
<!-- ================== -->
<!-- Input variables -->
<!-- ================== -->
<variableDef name="MachNumber" varID="XMACH"
varID="XMACH" units="" symbol="M">
<description>
Mach number (dimensionless)
</description>
<isStdAIAA/>
units="" symbol="M">
<description>
Mach number (dimensionless)
</description>
<isStdAIAA/> </variableDef>
<variableDef name="dbfll" varID="DBFLL" units="d"
</variableDef>
<variableDef name="dbfll" varID="DBFLL" units="d" sign="+TED"
sign="+TED" symbol="δbfll"
symbol="δbfll" >
<description>
Lower left body flap deflection, deg, +TED (so deflections are
always zero or positive).
</description>
</variableDef>
>
<description>
Lower left body flap deflection, deg, +TED (so deflections are
always zero or positive).
</description>
</variableDef>
 |
The |
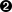 | The |
 | The optional |
 | The optional |
 | The optional |
 | The optional |
Example 3. A simple local variable
This DAVE-ML excerpt defines CRBFLLO which is the "independent
variable" output from the table lookup function shown in Example 11, “An excerpt giving the example of a function which refers to a previously defined
griddedTableDef” below.
<!-- ================== -->
<!-- Local variables -->
<!-- ================== -->
<!-- PRELIMINARY BUILDUP EQUATIONS -->
<!-- LOWER LEFT BODY FLAP CONTRIBUTIONS -->
<!-- table output signal -->
<variableDef name="Cldbfll_0" varID="CRBFLL0" units="">
<description>
Output of CRBFLL0 function; rolling moment contribution of
lower left body flap deflection due to alpha^0 (constant
term).
</description>
</variableDef>
Example 4. A more complete excerpt using a calculation element
Here the local variable CLBFLL is defined as a calculated quantity,
based on several other input or local variables (not shown). Note the description element is used to
describe the equation, in FORTRAN-ish human-readable text. The calculation element describes this
same equation in MathML-2 content markup syntax; this portion should be used by
parsing applications to create either source code, documentation, or run-time
calculation structures.
<!-- lower left body flap lift buildup -->
<variableDef name="CLdbfll" varID="CLBFLL" units="">
<description>
Lift contribution of lower left body flap deflection
CLdbfll = CLdbfll_0 + alpha*(CLdbfll_1 + alpha*(CLdbfll_2
+ alpha*CLdbfll_3))  </description>
<calculation>
</description>
<calculation>  <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML">
<apply>
<math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML">
<apply>  <plus/>
<ci>CLBFLL0</ci>
<apply>
<times/>
<ci>ALP</ci>
<apply>
<plus/>
<ci>CLBFLL1</ci>
<apply>
<times/>
<ci>ALP</ci>
<apply>
<plus/>
<ci>CLBFLL2</ci>
<apply>
<plus/>
<ci>CLBFLL0</ci>
<apply>
<times/>
<ci>ALP</ci>
<apply>
<plus/>
<ci>CLBFLL1</ci>
<apply>
<times/>
<ci>ALP</ci>
<apply>
<plus/>
<ci>CLBFLL2</ci>
<apply>  <times/>
<ci>ALP</ci>
<ci>CLBFLL3</ci>
</apply> <!-- a*c3 -->
<times/>
<ci>ALP</ci>
<ci>CLBFLL3</ci>
</apply> <!-- a*c3 -->  </apply> <!-- (c2 + a*c3) -->
</apply> <!-- a*(c2 + a*c3) -->
</apply> <!-- (c1 + a*(c2 + a*c3)) -->
</apply> <!-- a*(c1 + a*(c2 + a*c3)) -->
</apply> <!-- c0 + a*(c1 + a*(c2 + a*c3)) -->
</math>
</calculation>
</variableDef>
</apply> <!-- (c2 + a*c3) -->
</apply> <!-- a*(c2 + a*c3) -->
</apply> <!-- (c1 + a*(c2 + a*c3)) -->
</apply> <!-- a*(c1 + a*(c2 + a*c3)) -->
</apply> <!-- c0 + a*(c1 + a*(c2 + a*c3)) -->
</math>
</calculation>
</variableDef>
Example 5. An output variable based on another calculation element
This excerpt is an example of how an output variable (CL) might be
defined from previously calculated local variables (in this case,
CL0, CLBFL, etc.).
<!-- ================== -->
<!-- Output variables -->
<!-- ================== -->
<variableDef name="CL" varID="CL" units="" sign="+UP" symbol="CL">
<description>
Coefficient of lift
CL = CL0 + CLBFUL + CLBFUR + CLBFLL + CLBFLR +
CLWFL + CLWFR + CLRUD + CLGE + CLLG
</description>
<calculation>
<math>
<apply>  <plus/>
<ci>CL0</ci>
<ci>CLBFUL</ci>
<ci>CLBFUR</ci>
<ci>CLBFLL</ci>
<ci>CLBFLR</ci>
<ci>CLWFL</ci>
<ci>CLWFR</ci>
<ci>CLRUD</ci>
<ci>CLGE</ci>
<ci>CLLG</ci>
</apply>
</math>
</calculation>
<isOutput/>
<plus/>
<ci>CL0</ci>
<ci>CLBFUL</ci>
<ci>CLBFUR</ci>
<ci>CLBFLL</ci>
<ci>CLBFLR</ci>
<ci>CLWFL</ci>
<ci>CLWFR</ci>
<ci>CLRUD</ci>
<ci>CLGE</ci>
<ci>CLLG</ci>
</apply>
</math>
</calculation>
<isOutput/>  </variableDef>
</variableDef>
Example 6. An intermediate variable with a calculation element that uses a
DAVE-ML extension (atan2) to the standard MathML function set
In this excerpt, we demonstrate a means to encode a non-standard MathML-2 math function,
atan2. The atan2 function is used often in C, C++, Java and other modeling languages and
has been added to the DAVE-ML standard by use of the MathML csymbol
element, specifically provided to allow extension of MathML for cases such as this.
<!-- ================== -->
<!-- ATAN2 example -->  <!-- ================== -->
<variableDef name="Wind vector roll angle" varID="PHI" units="r">
<description>
This encodes the equation PHI = atan2( tan(BETA), sin(ALPHA) ) where atan2
is the two-argument arc tangent function from the ANSI C standard math
library; the first argument represents the sine component and the second
argument is the cosine component.
</description>
<calculation>
<math>
<apply>
<csymbol definitionURL="http://daveml.nasa.gov/function_spaces.html#atan2"
encoding="text">
<!-- ================== -->
<variableDef name="Wind vector roll angle" varID="PHI" units="r">
<description>
This encodes the equation PHI = atan2( tan(BETA), sin(ALPHA) ) where atan2
is the two-argument arc tangent function from the ANSI C standard math
library; the first argument represents the sine component and the second
argument is the cosine component.
</description>
<calculation>
<math>
<apply>
<csymbol definitionURL="http://daveml.nasa.gov/function_spaces.html#atan2"
encoding="text">  atan2
</csymbol>
<apply>
<tan/>
<ci>BETA</ci>
atan2
</csymbol>
<apply>
<tan/>
<ci>BETA</ci>  </apply>
<apply>
<sin/>
<ci>ALPHA</ci>
</apply>
<apply>
<sin/>
<ci>ALPHA</ci>  </apply>
</apply>
</math>
</calculation>
</variableDef>
</apply>
</apply>
</math>
</calculation>
</variableDef>
 | This excerpt shows how to calculate wind roll angle, phi, from angle of attack and angle of sideslip; it comes from the Apollo aero data book [NAA64]. |
 |
The |
 |
BETA is the |
 |
ALPHA is the |